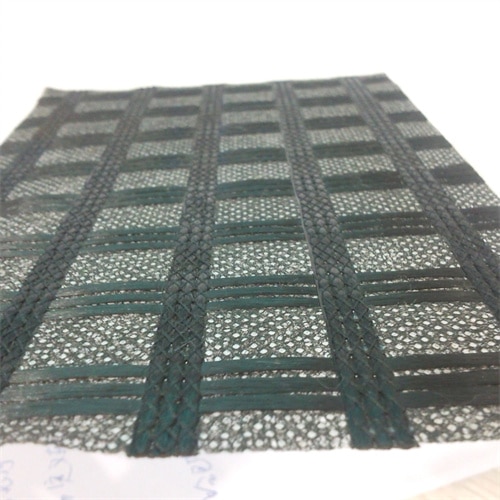
What is a Fiberglass Geocomposite? Key Benefits, Uses, and Installation Guide
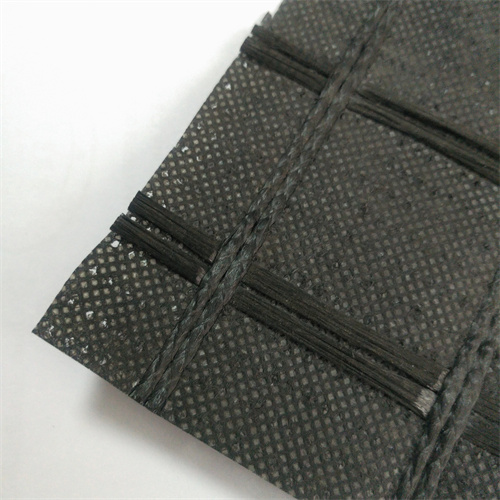
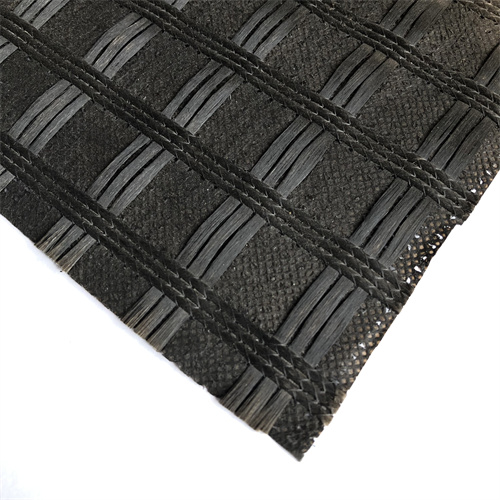
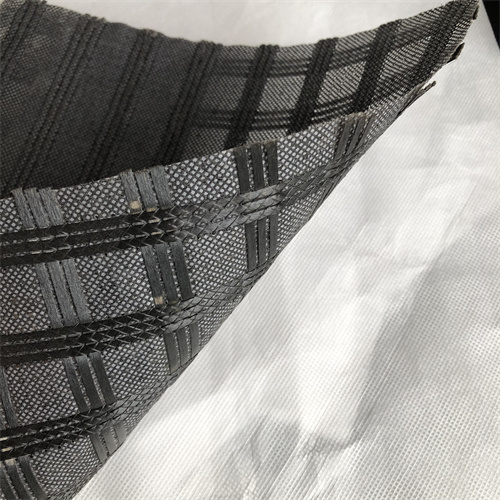
A fiberglass geocomposite is a high-performance engineered material combining fiberglass reinforcement grids with geosynthetic layers (geotextiles or geomembranes). Designed for durability and versatility, it is widely used in civil engineering, construction, and environmental projects to enhance soil stability, drainage, and load distribution.
Why Fiberglass Geocomposite? Top 6 Advantages
- Superior Strength & Durability
Fiberglass grids provide exceptional tensile strength (up to 200 kN/m) while resisting corrosion, UV degradation, and chemical exposure—ideal for harsh environments. - Lightweight & Easy to Install
Weighing 50% less than steel alternatives, fiberglass geocomposites reduce labor costs and accelerate project timelines. - Enhanced Soil Stabilization
Prevents soil erosion and subsidence by distributing loads evenly across weak or uneven terrain. - Cost-Effective Longevity
With a lifespan exceeding 50 years, it minimizes maintenance costs for roads, slopes, and retaining walls. - Eco-Friendly Solution
Reduces the need for quarry materials and lowers carbon footprints in infrastructure projects. - Multi-Functional Design
Combines drainage, filtration, and reinforcement in a single layer, streamlining construction processes.
Separation Drainage
Filtration Reinforcement
Applications of Fiberglass Geocomposite
- Road & Railway Construction: Stabilizes subgrades, reduces rutting, and extends pavement life.
- Slope & Embankment Reinforcement: Prevents landslides in hilly or coastal areas.
- Landfill Liners & Drainage Systems: Ensures leak-proof containment and efficient fluid management.
- Retaining Walls & Bridge Abutments: Enhances structural integrity under heavy loads.
- Erosion Control: Protects shorelines, riverbanks, and mining sites.
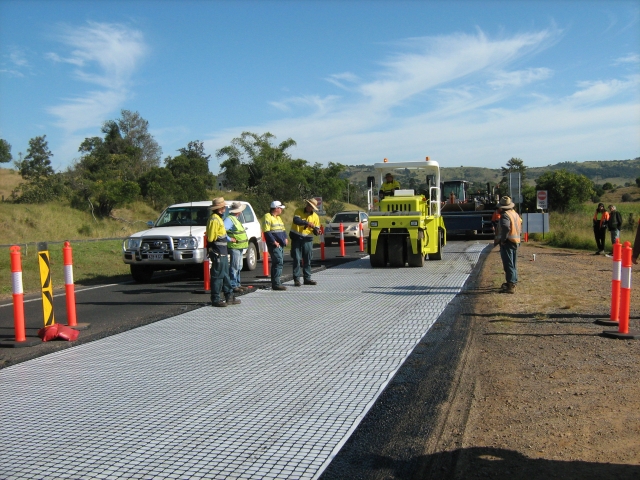

How Does Fiberglass Geocomposite Work?
- Load Distribution: The fiberglass grid absorbs and redistributes stress, preventing soil movement.
- Drainage & Filtration: Geotextile layers allow water to pass through while blocking soil particles.
- Barrier Protection: Geomembranes act as impermeable liners for containment applications.
Installation Best Practices
- Site Preparation: Clear debris, level the ground, and compact the subsoil.
- Unrolling & Alignment: Lay the geocomposite with overlaps (10–12 inches) and secure edges with stakes or adhesive.
- Backfilling: Cover immediately with aggregate or soil to avoid UV exposure damage.
- Quality Checks: Ensure seams are sealed and alignment matches design specifications.